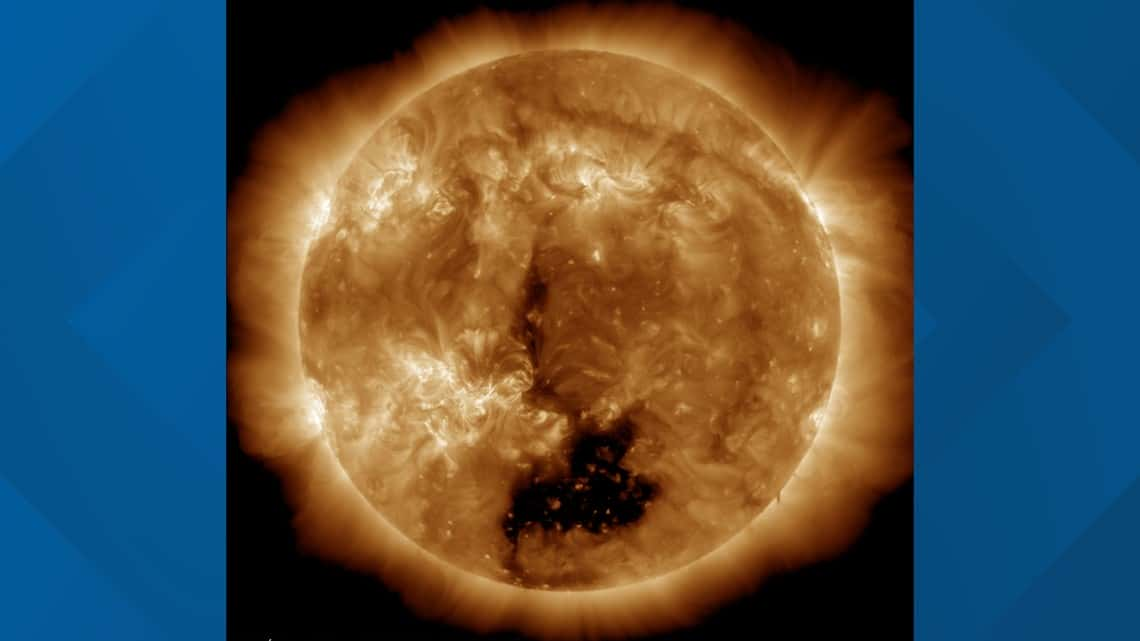
Discovered near the sun’s equator on December 2, this gigantic sun coronal hole expanded to a width exceeding 60 Earths, reaching a maximum span of approximately 497,000 miles within a mere 24 hours, as reported by Spaceweather.com.
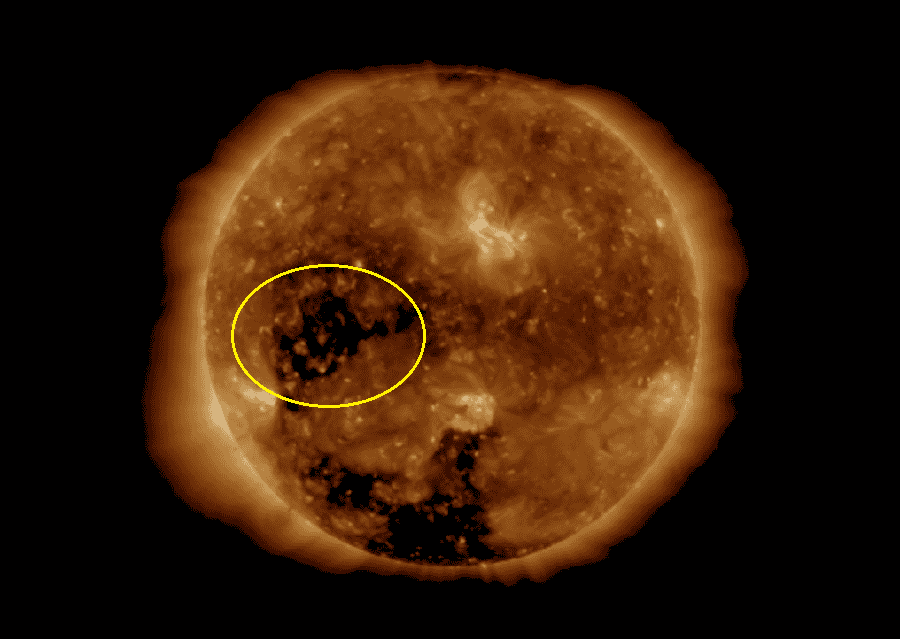
In an unprecedented celestial event, a colossal dark opening, identified as a sun coronal hole, has manifested on the sun’s surface, emitting potent streams of high-speed solar wind directly toward Earth
Since December 4, Earth has found itself in the direct line of the solar void. Initially projected to incite a moderate (G2) geomagnetic storm, capable of inducing radio blackouts and vivid auroras, the solar wind’s intensity has fallen short of expectations. Consequently, the resulting storm has only attained a weak (G1) classification so far, according to Spaceweather.com. Although auroras remain plausible at high latitudes, the duration of sun coronal hole’s presence in the sun remains uncertain.
Sun coronal holes, formed when magnetic fields on the sun unexpectedly open, expelling solar wind, appear as dark patches due to their cooler and less dense nature compared to surrounding plasma
Although typically more prevalent during solar minimum, this massive equatorial sun coronal hole challenges expectations, as solar activity has been escalating throughout the year, leading scientists to anticipate the imminent solar maximum peak in early 2024. Recent indicators of heightened solar activity include a sunspot archipelago, a fiery canyon eruption, and powerful solar flares. Despite the mystery surrounding the equatorial sun coronal hole’s appearance, it signals a dynamic phase in the sun’s activity.




