In a remarkable celestial event, forecasters are now anticipating that the solar activity associated with this extraordinary flare could generate auroras as far south as New York in the East and Idaho in the West in the coming days.
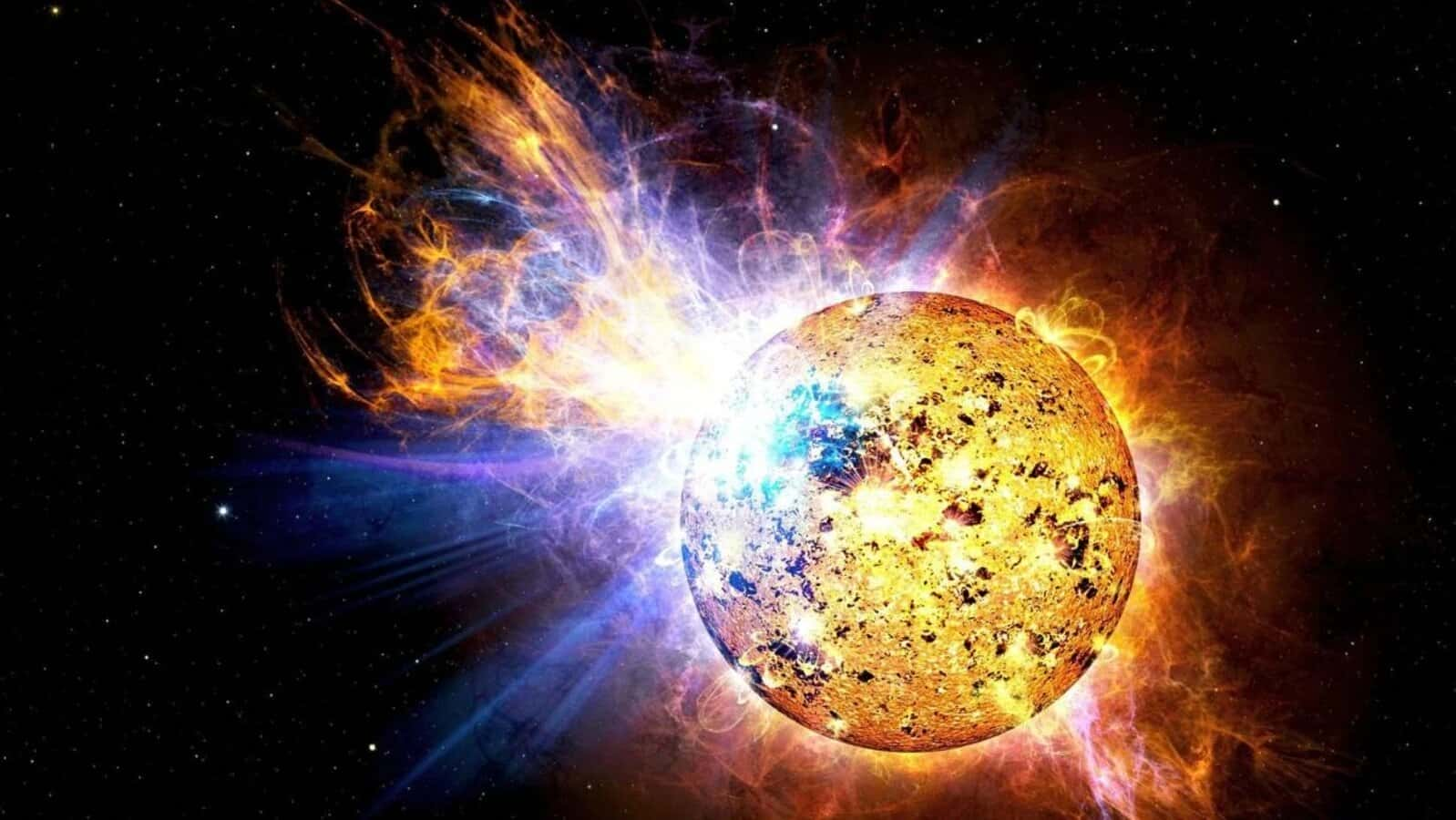
The strongest solar flare in over six years erupted from the sun on Thursday afternoon, leading to widespread radio blackouts on Earth, particularly in South America
SpaceWeather.com has labeled this occurrence as the strongest solar flare of Solar Cycle 25, marking it as the most potent solar eruption since the notable storms of September 2017. The Space Weather Prediction Center, a division of NOAA, has termed it an “amazing event” and potentially “one of the largest solar radio events ever recorded.” The interference with radio communications, including aviation signals, has been reported across the nation, emphasizing the far-reaching impact of this solar phenomenon.
This latest strongest solar flare, classified as an X2.8 flare, falls under the category of X-class flares, denoting the most intense solar bursts. The number provides additional insight into the flare’s strength. Furthermore, the prediction center is closely monitoring a potential Earth-directed coronal mass ejection linked to this flare. Coronal mass ejections, described as clouds of electrified, magnetic gas expelled from the sun, can travel through space at speeds ranging from 12 to 1,250 miles per second. These ejections have the potential to induce geomagnetic storms on Earth, leading to the creation of awe-inspiring auroras.
Forecasters from the Space Weather Prediction Center have issued an alert for a G2 “moderate” level geomagnetic storm for both Saturday and Sunday, with the possibility of auroras visible as far south as New York and Idaho
This heightened solar activity is part of a larger trend, with predictions suggesting that solar forces producing auroras are set to peak next year at a more intense level than previously anticipated. The updated forecast now places the peak of Solar Cycle 25 between January and October of 2024, indicating a quicker and more substantial increase in strongest solar flare activity than initially projected in December 2019.