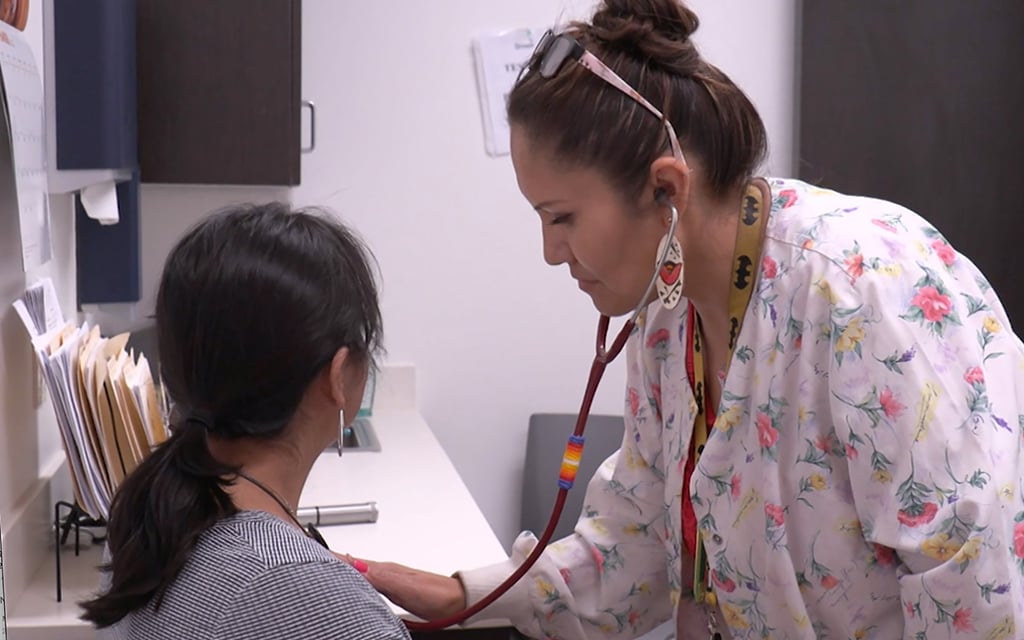
While COVID-19, RSV, and the flu continue to rise, health officials in the eastern United States are currently dealing with whooping cough, or pertussis, epidemics. There have been student case reports from Stroudsburg, Pennsylvania, and Suffolk County, New York, which prompted parent alerts. Notably, Suffolk County noted that school-age children and their parents who had received vaccinations accounted for the majority of the 108 cases. Health agencies emphasize the significance of early identification and antibiotic treatment to stop the spread of pertussis, despite the illness’s resemblance to other respiratory infections.

Antibiotic Therapy and Contagiousness
Pertussis, unlike several respiratory diseases, can be treated with medication if caught early. Individuals in households where a case has been reported should take antibiotics to prevent further transmission. Pertussis is caused by the bacteria Bordetella pertussis and is extremely contagious, with illness particles easily spread through the air, particularly when coughing or sneezing.
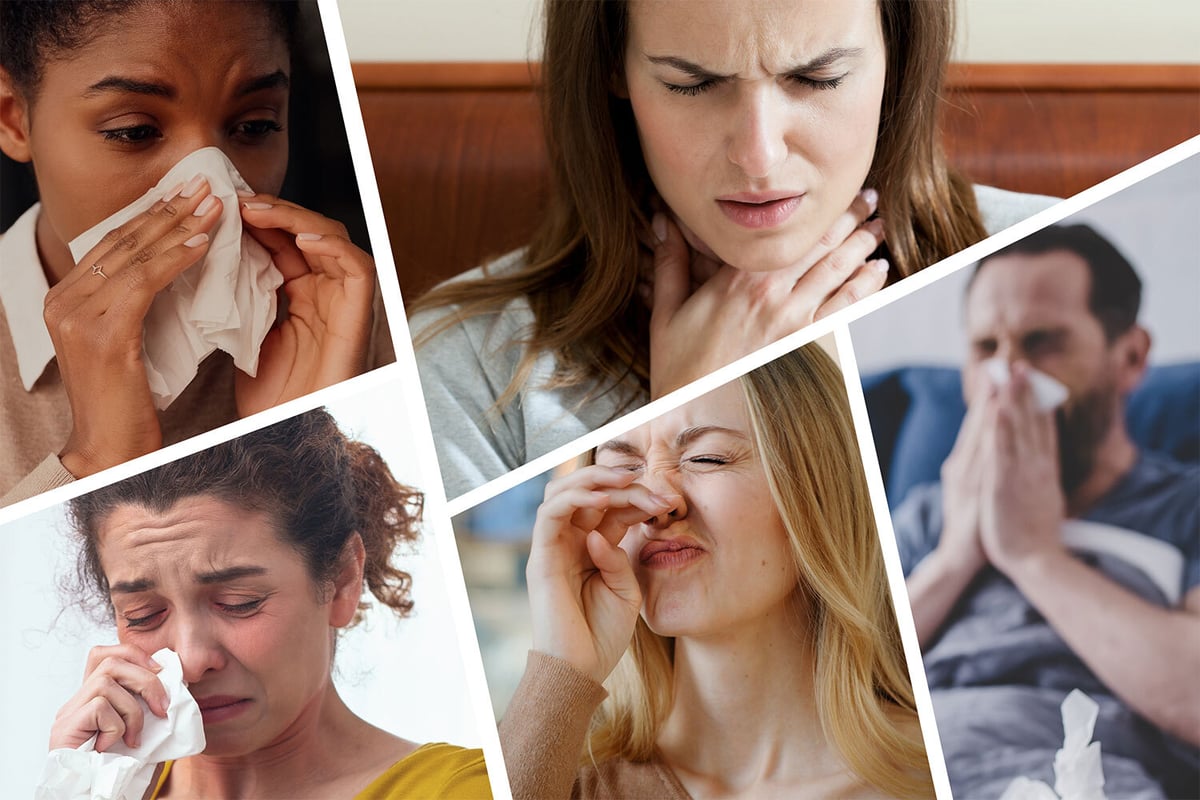
Pertussis exhibits symptoms similar to a common cold initially, making early diagnosis challenging. Severe symptoms, such as uncontrollable coughing fits lasting up to 10 weeks, may appear one to two weeks later. Infants, in particular, may not exhibit coughing but can experience life-threatening complications, including apnea and pneumonia.
READ ALSO: Revolutionary Weight Loss Pill: Cheap Solution for Shedding Pounds without Giving Up Junk Food
Reporting Challenges and Prevention
Limitations in diagnostics and reporting challenges often leave pertussis cases undiagnosed and unreported. Despite lower case numbers in 2020-2022, the reported cases in 2023 were more than double, prompting health officials to emphasize prevention efforts.
Antibiotics and vaccination, particularly the DTaP for children under 7 and Tdap for those above 7, are recommended by the CDC to prevent or mitigate the severity of pertussis. Pregnant women in their third trimester can also receive the Tdap vaccine to pass antibodies to their newborns.