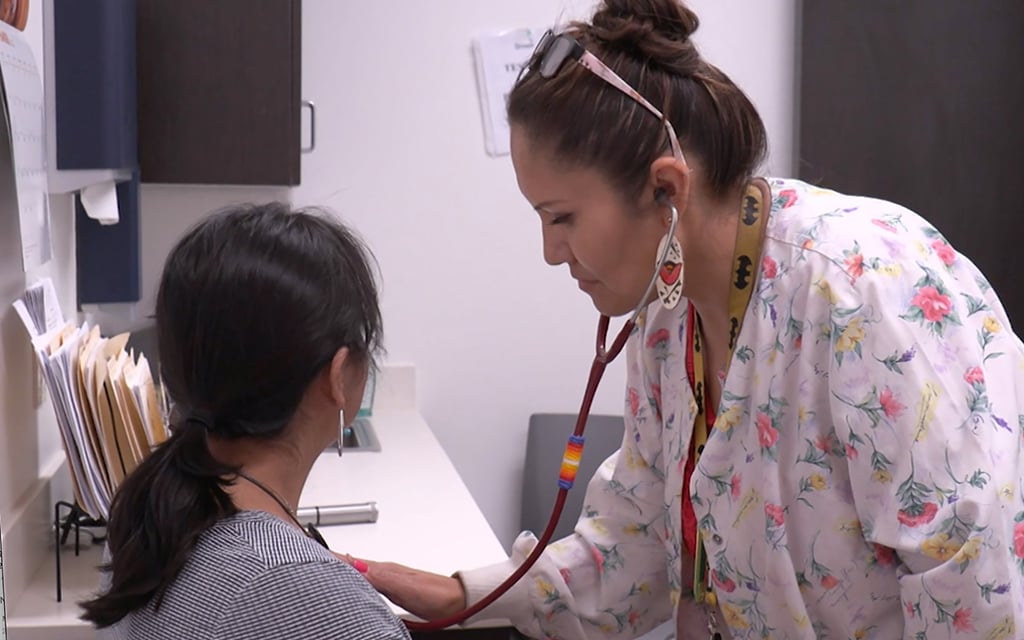
A revolutionary mouse study found that urea-powered nanorobots reduce bladder cancers by 90%. This bladder cancer therapeutic breakthrough is led by IBEC and CIC biomaGUNE. Bladder cancer is the fourth most common male malignancy worldwide. A potential cancer treatment using nanorobots, self-propelling nanoparticles, is investigated.
Urea-Powered Nanorobots Propel Hope in Bladder Cancer Treatment!
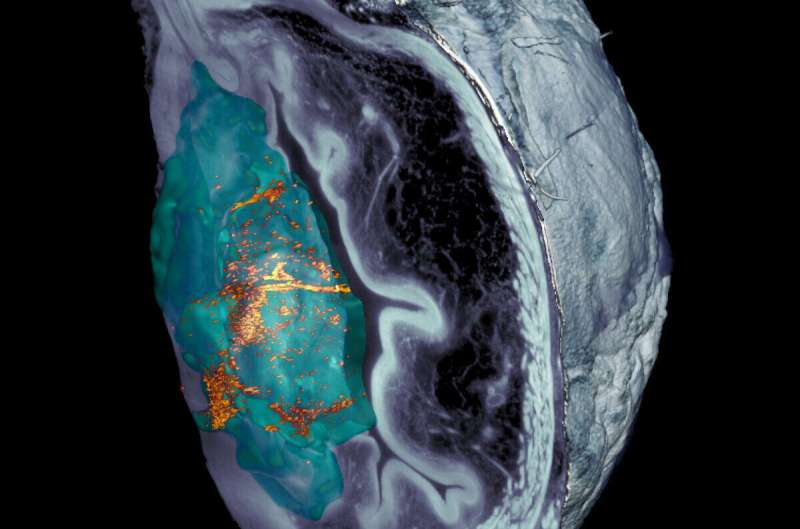
These porous silica nanorobots propel themselves by reacting with urine urea using urease. Radioactive iodine, a limited tumor therapy radioisotope, is also important. In mice, a single injection of urea-powered nanorobots reduced bladder tumor volume by 90%. Direct medication administration for bladder cancer offers minimal efficacy. Nanoparticles, especially self-propelled nanorobots, are intriguing alternatives. The Nature Nanotechnology shows how nanorobots could revolutionize bladder cancer treatment.
The urease-urea interaction drove nanorobots through the bladder with extraordinary motility. Nanorobots reached all bladder walls well, unlike previous treatments that required repeated patient position adjustments. Additionally, the study highlighted their tumor-specific accumulation, improving radioisotope treatment.
Researchers used PET imaging and fluorescence microscopy to monitor nanorobot motion and tumor penetration. The study showed their ability to infiltrate the tumor and accumulate inside, addressing a critical cancer therapeutic issue.
READ ALSO: NASA Addresses Allegations Against Elon Musk Involving Drugs
Nanorobots: Breakthrough Discovery in Bladder Cancer Treatment Promises Precision Attack on Tumors!
Key discovery: nanorobots’ ability to break down tumor extracellular matrix by locally elevating pH through a self-propelling chemical process. Due to their mobility, nanorobots could infiltrate and accumulate inside tumors without antibodies.
Nanorobots carrying the radioisotope were locally administered, reducing side effects and improving radiotherapy. The study prepares for innovative bladder cancer treatments to cut hospitalizations, expenses, and patient discomfort.
The three-year collaboration included IBEC, CIC biomaGUNE, IRB Barcelona, and the Autonomous University of Barcelona. Nanobot Therapeutics, a January 2023 spin-off, was created from the innovative technology. Samuel Sánche z founded this company to bridge research and clinical application, focusing on technology and market execution.