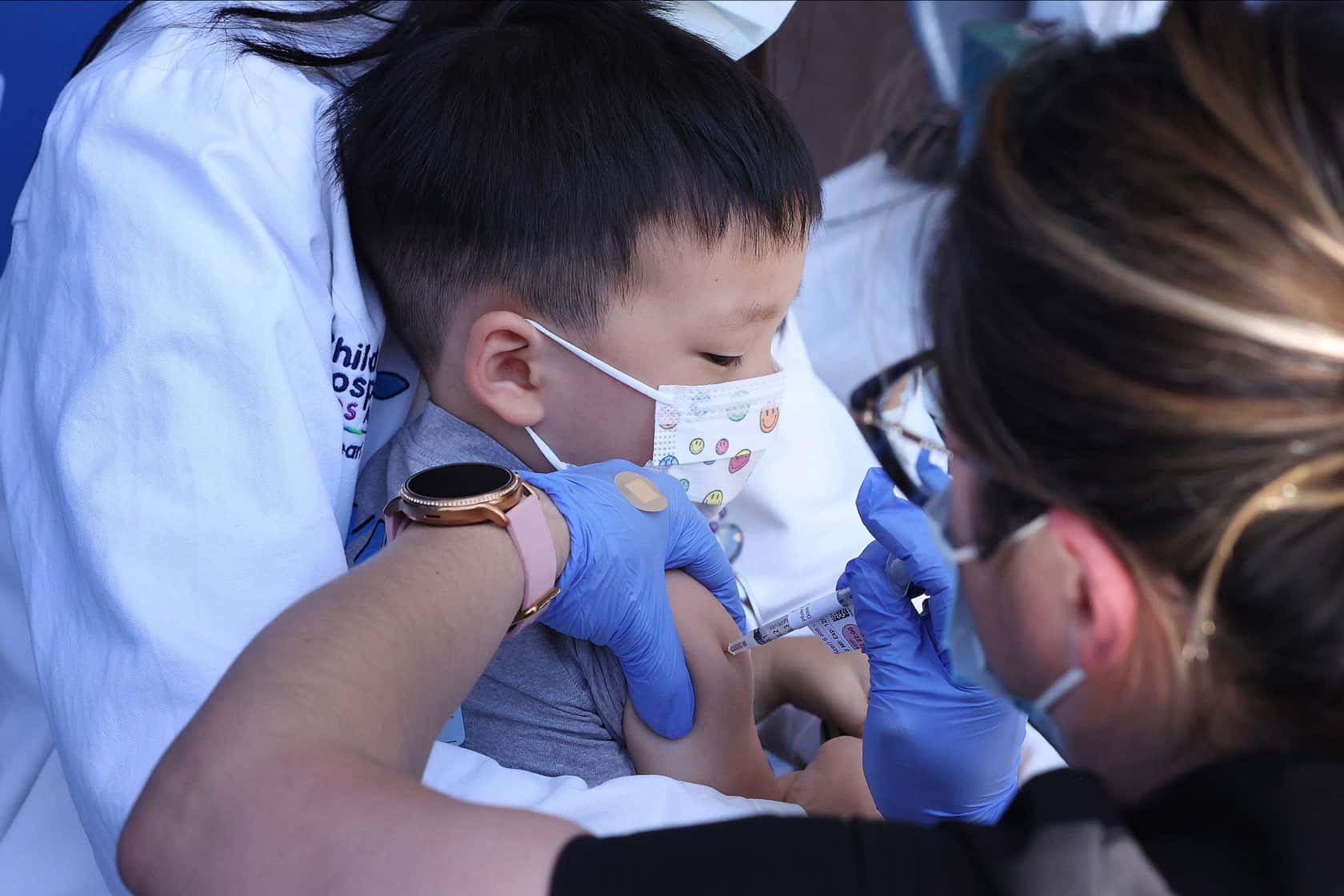
How can the rising childhood vaccine exemptions increase the risk of young children getting contagious and severe diseases?
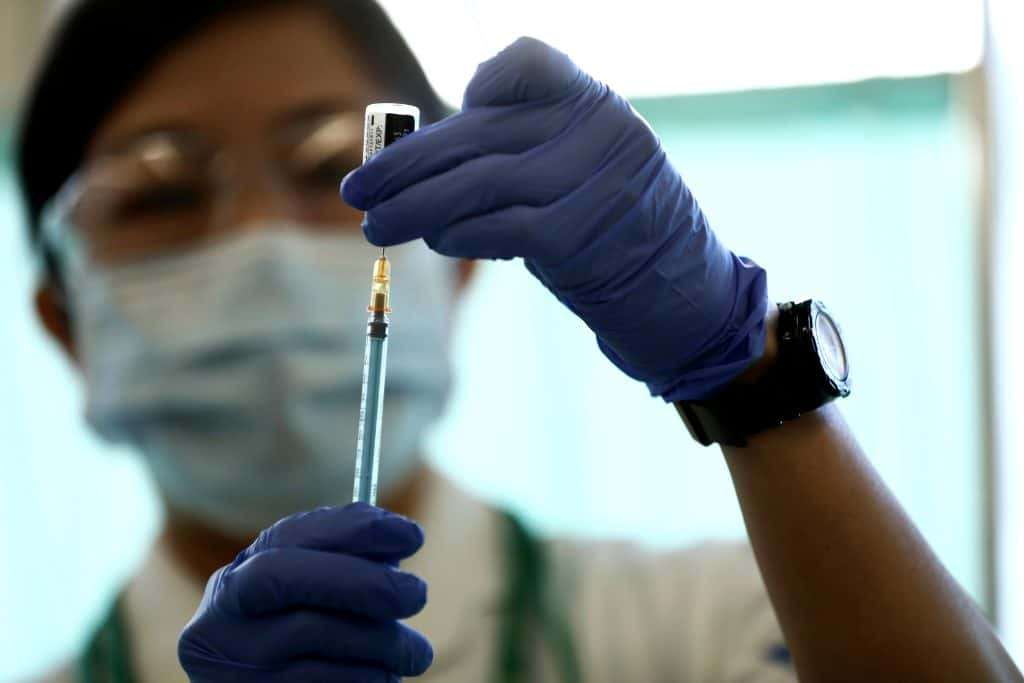
Rising Number of Childhood Vaccine Exemptions to Increase Risk of Young Children Getting Contagious and Severe Diseases
The rising number of childhood vaccine exemptions will reportedly increase the risk of young children getting contagious and severe diseases even more as the reported childhood vaccine exemptions have already reached the highest level in the latest statistics.
According to a report published in US News, the rising number of childhood vaccine exemptions means that young children are not entirely immune from contagious and severe diseases, including measles and polio despite all states requiring them to be vaccinated, increasing the childhood vaccine exemptions.
Despite the high risk to young children, the childhood vaccine exemptions continued to increase for various reasons; however, health experts encouraged parents to get their children vaccinated to ensure their safety because as the childhood vaccine exemptions increased, the risk surrounding them also increased.
READ ALSO: Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccine Shortage Spurs Revised Recommendations For Infant Protection
Several Factors Fueling Vaccine Hesitancy and Increasing Number of Childhood Vaccine Exemptions
With the increasing number of childhood vaccine exemptions, several factors fuel the vaccine hesitancy of parents, including political, religious, and other nonmedical reasons, especially after the pandemic.
Aside from nonmedical reasons, several parents have been hesitating to get their young children vaccinated as they are scared that vaccines will only negatively affect their children’s health, increasing the childhood vaccine exemptions, AP News reported.