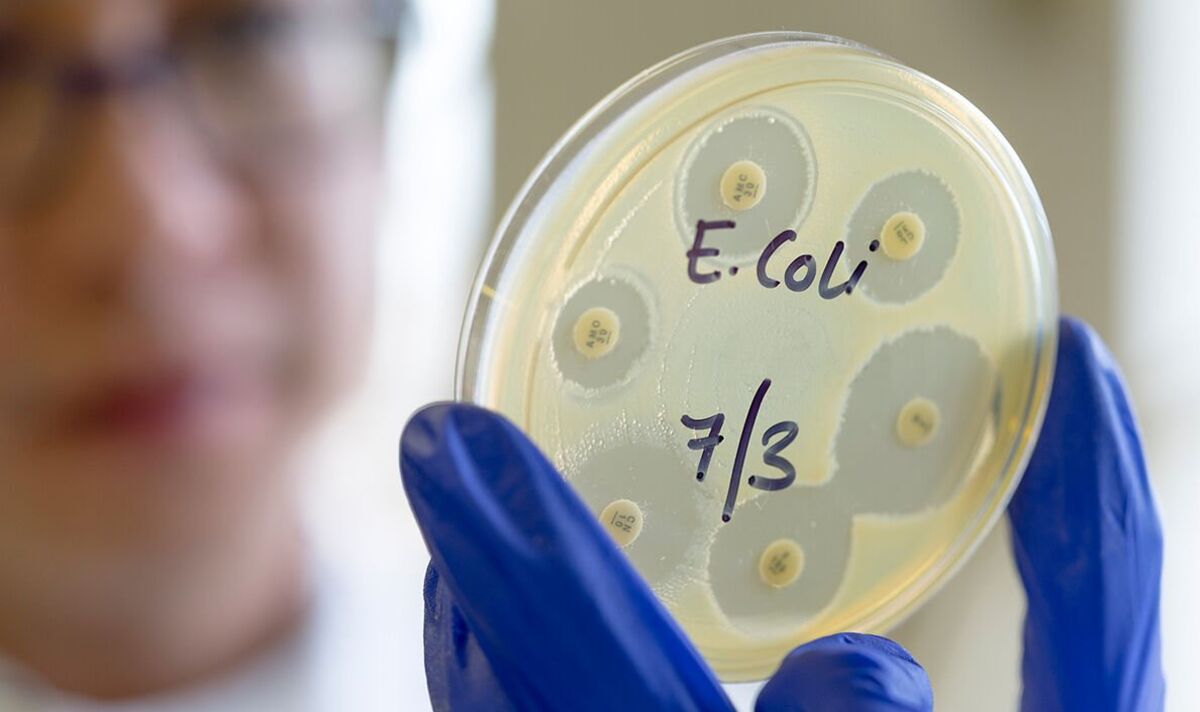
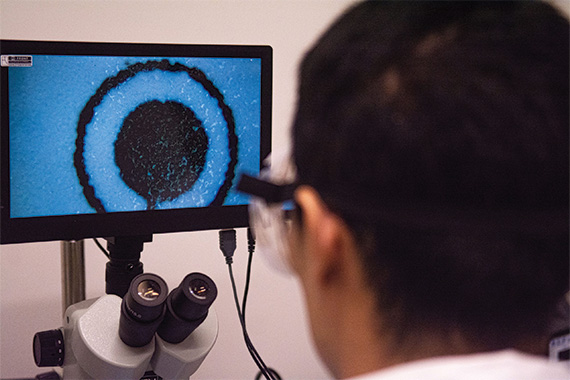
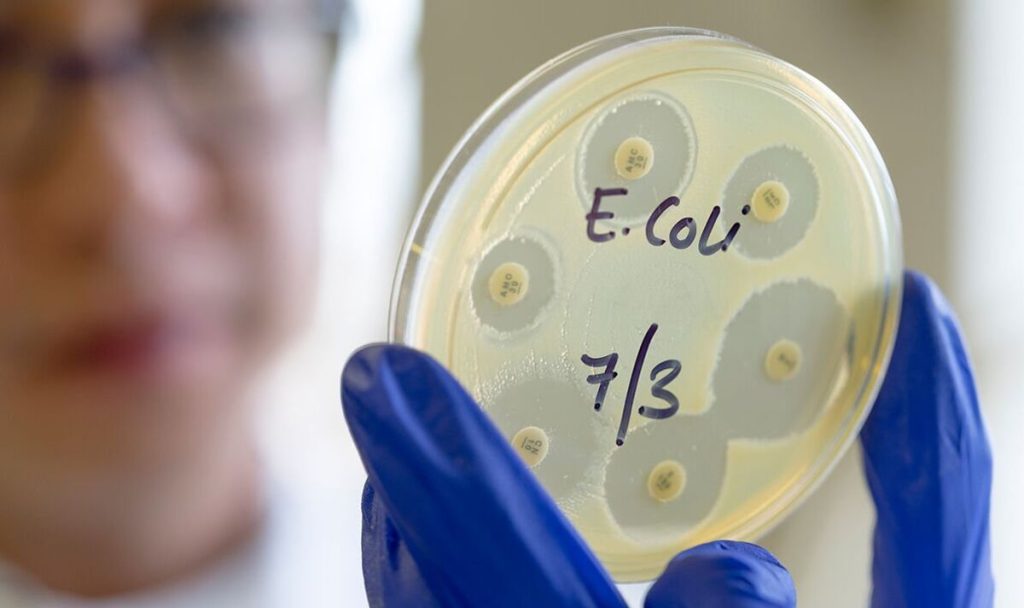
An E. coli outbreak in England and Scotland linked to cheese products has resulted in one death and 30 reported cases since July, according to the UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA). The Food Standards Agency (FSA) has issued a recall for four products from Mrs. Kirkham’s Lancashire Cheese due to contamination fears. The affected individuals, aged seven to 81, highlight the severity of the situation. Understanding E. coli, its dangers, and symptoms becomes crucial in the face of this outbreak.
E. Coli, Symptoms and Severity
E. coli is a versatile bacterium, with some strains playing a vital role in digestion, while others can be harmful. The pathogenic strains, such as E. coli O157, are responsible for outbreaks and can lead to severe foodborne illnesses. In Scotland’s recent outbreak, understanding the specific strain involved is crucial for effective containment and treatment.
Thorrun Govind, a pharmacist and health expert, outlines varying symptoms of STEC infection, ranging from mild diarrhea to severe abdominal cramps, vomiting, and bloody diarrhea. Symptoms typically surface three to four days after exposure but can appear within one to ten days. Govind advises isolation for 48 hours from symptom onset, proper handwashing, and avoiding food preparation for others to curb bacterial spread.
Five to ten percent of people may face life-threatening complications or death due to STEC, with decreased urination, extreme fatigue, and loss of skin color as alarming signs. Up to 15% of cases may develop haemolytic uraemic syndrome (HUS), a serious kidney condition that can be fatal, particularly in young children and vulnerable groups like the elderly.
READ ALSO: Reassessing Pandemic Responses: Public Health Officials Acknowledge Limitations
Treatment and Recommendations
No particular therapy for E is mentioned by Public Health England (PHE). coli, stressing that the sickness usually goes away in a week or so. It’s critical to stay hydrated to avoid dehydration brought on by diarrhea. Antibiotics are discouraged by PHE since they can worsen issues like HUS.
As the E. coli outbreak unfolds in the UK, awareness of symptoms, preventive measures, and potential complications becomes paramount. Following recommended guidelines, such as isolation and proper hygiene, is crucial in limiting the spread of this bacterial infection. Authorities, health agencies, and the public’s collective efforts are vital in managing the outbreak and safeguarding public health.
READ ALSO: Measles Exposure Warning Issued in Center City: Philadelphia Health Officials